During typical earth fault conditions, the flow of current to the earth will produce voltage gradients within and around a substation.
The image below shows the ground surface voltages during a 50/60 Hz earth fault for a 110 kV AIS/GIS substation earth grid buried within a soil resistivity structure which has multilayers.
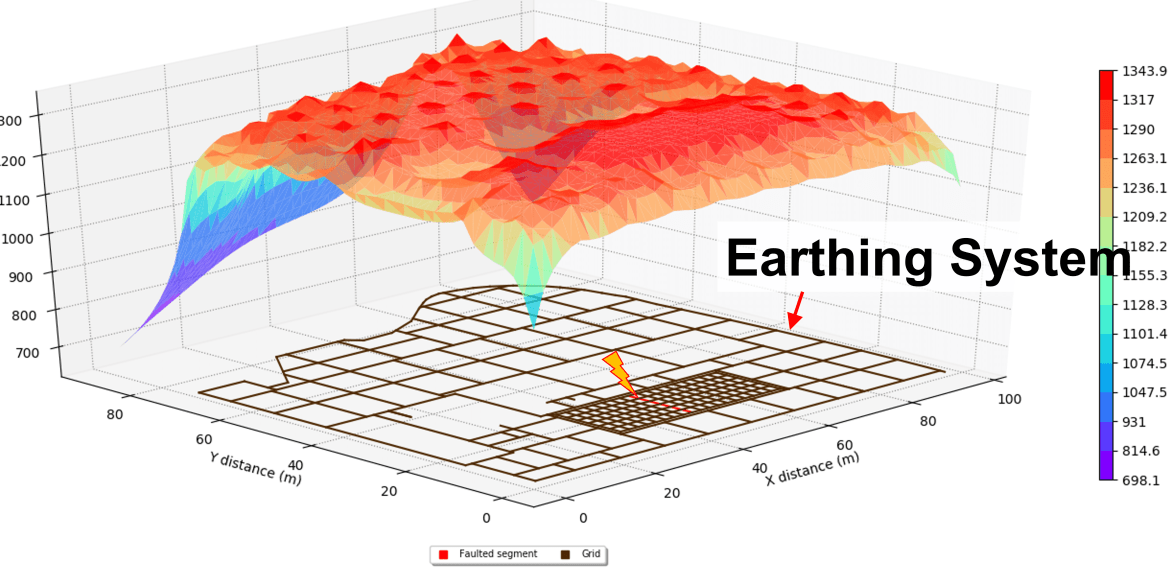
The following plots demonstrate the behaviour of the grid conductors (in terms of currents distribution and voltage rise) as the fault energy is dissipated into the surrounding soil.
The plots shown were produced using ELEK SafeGrid Earthing Software.
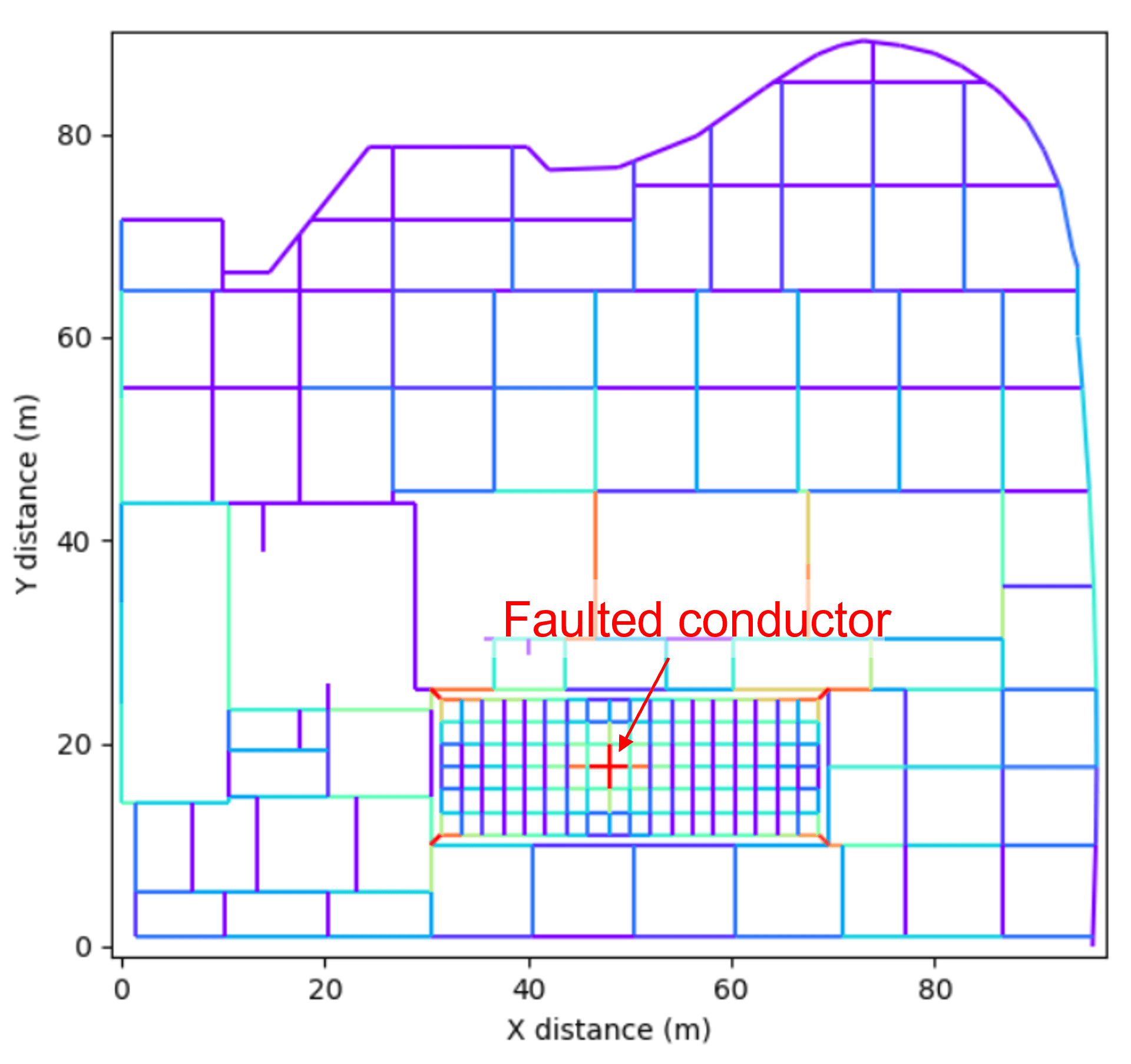
Longitudinal currents
The plot here shows the magnitudes of the currents travelling along each grid conductor. The hot colours (where red colour is the hottest) indicates high current magnitude.
The total fault current enters the earth grid at the faulted conductor in the GIS building (centre of the plot). The fault current divides as it travels through the grid conductor network.
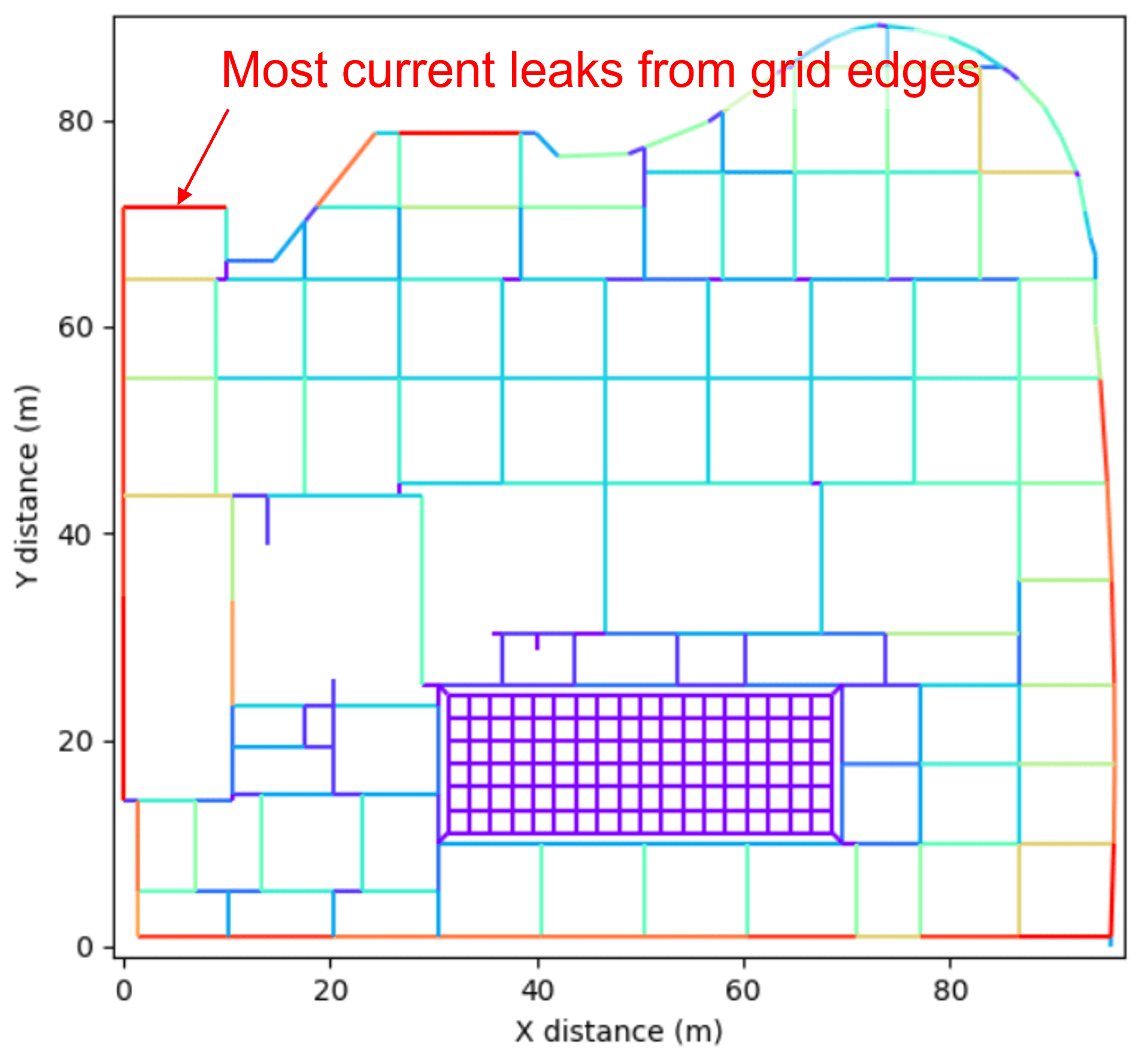
Leakage currents
This plot shows the currents leaking out of conductors into the surrounding soil.
Most of the fault current is dissipated into the soil along the perimeter conductors. This is one reason why the highest touch voltage hazards are often seen at the grid perimeters.
Segment voltages
This plot shows the voltage magnitude of the grid conductors.
As expected, the highest voltages are seen at the conductors nearest to the fault location (injection point). There is a voltage drop across each of the conductors which reduces the voltages of conductors that are farther from the injection point.









