Free Calculators
Cable Sizing AS3008 Calculator
Cable Sizing BS7671 Calculator

Voltage Drop Calculator

Arc Flash Calculator
Earth Cable Sizing Calculator

Fault Loop Impedance Calculator
Earth Grid Resistance Calculator

Earth Grid Conductor Sizing

Earthing Rods Resistance Calculator

Lightning Protection Design
Relay Tripping Time Calculator
Equivalent Thermal Resistance

Cable Sizing AS3008 Calculator

Cable Sizing BS7671 Calculator

Voltage Drop Calculator

Arc Flash Calculator

Earth Cable Sizing Calculator

Fault Loop Impedance Calculator

Earth Grid Resistance Calculator

Earth Grid Conductor Sizing

Earthing Rods Resistance Calculator

Lightning Protection Design

Relay Tripping Time Calculator

Equivalent Thermal Resistance
Voltage Drop Calculator
This calculator uses the accurate voltage drop equations from AS/NZS 3008.1. Accurate voltage drop calculations result in smaller cable sizes.
Read the FAQ section below for helpful tips.
Your Calculated Voltage Drop Is:
The current ratings, cable resistance and cable reactance values used by this calculator were taken from AS/NZS 3008.1.1:2017 (based on IEC Standards).
Professional Electrical Design Software
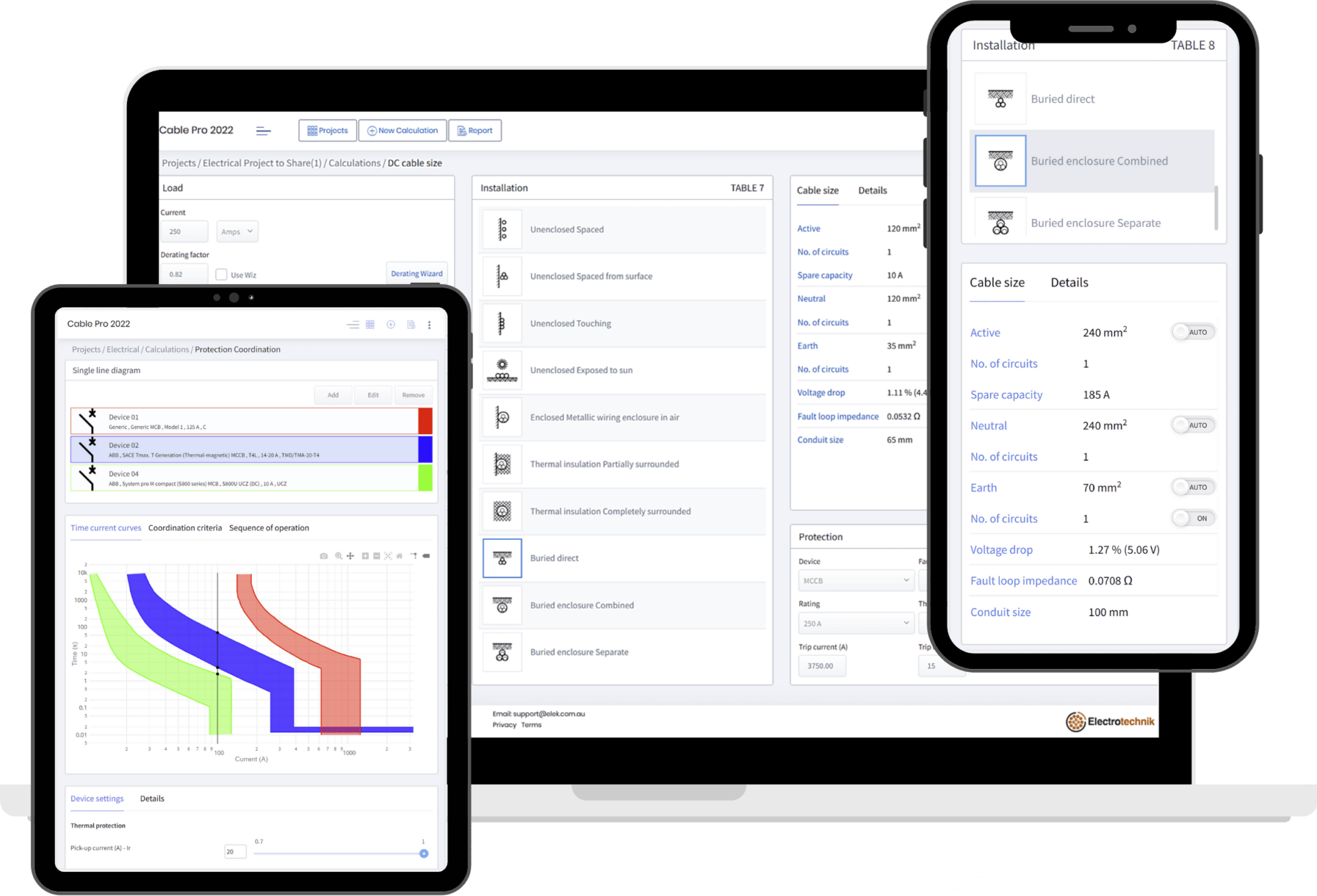
Cable Pro Software can do all the necessary electrical calculations and produce reports. Comprehensive Cloud-Based Software for Cable Sizing, Maximum Demand Calculations, Protection, Arc Flash Analysis, and LV Network Design

Expert tips for voltage drop calculations
Frequently asked questions
What is voltage drop and why is it important?
Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage as electrical current flows through the cables. It is critical in electrical installations because excessive voltage drop can cause equipment malfunction, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards. The Australian and New Zealand standard AS/NZS 3008.1 provides equations to calculate voltage drop accurately and a step-by-step procedure for low-voltage cable sizing calculations.
How do I calculate voltage drop?

Allowable voltage drop limits?
How to convert power or horsepower into current?
The equations to convert the units of the electrical load inputs used by the calculator are as follows.
How do I calculate voltage rise instead of voltage drop?
- Voltage rise is not different to voltage drop calculations.
- Voltage rise occurs in solar PV systems on the AC side between the power inverters and the network connection when power flows from the inverter back into the network.
- Australian standards and state regulations cover the requirements and limits for voltage rise. Refer to the article Voltage rise calculations.
- Cable Pro Software has a selection for voltage rise (%).
How do I enter a 3-phase load current?
- The load current you enter for the cable sizing calculations is the maximum load current per phase.
- So for a 3 phase supply the load current would be the load on the phase which carries the highest load current (highest loaded phase).
What should I enter for power factor?
- Poor power factor affects cable size significantly because it increases voltage drop, especially for large cables (they have high reactance).
- The Service and Installation Rules of New South Wales require that an electrical installation must have a power factor of 0.9 or greater lagging.
How do I calculate the voltage drop for an unbalanced 3-phase system?
If the out-of-balance conditions are inconsistent or intermittent:
- An approach to calculating the voltage drop for an unbalanced three-phase load is to assume a balanced three-phase load condition and perform calculations using the current flowing in the heaviest-loaded phase.
Where the currents in each phase are different in magnitudes for consistent periods:
- In this case, voltage drop calculations can be performed by selecting phases as single-phase.
Calculator inputs explained
Voltage (V)
- The voltage is used to calculate the actual percentage voltage drop.
- By default, the supply voltage is 230 V for single phase and 400 V for 3-phase loads.
- The nominal voltage for low-voltage systems and electrical installations is 230/400 V, as per the Wiring Rules AS/NZS 3000:2018.
Phase
- Select the phase arrangement to match the load. The options available are single-phase AC, three-phase AC, two-phase AC, or DC.
- This phase arrangement affects the voltage drop calculation because different voltage drop equations are used.
- Three-phase AC is used for larger loads and consumer mains. Balanced three-phase conditions are assumed, meaning the current in each of the three phases is the same.
- To calculate the voltage drop for an unbalanced three-phase load, a conservative approach is to assume a balanced three-phase load condition and perform calculations using the current flowing in the heaviest-loaded phase.
Load
- The load determines the current-carrying capacity of the cable. The load is specified in Amps, kilowatts, kVA, or horsepower.
- For a three-phase load, this should be the current of the highest-loaded phase or the total power on all the phases.
Power factor
- Enter the load power factor (assumed lagging). The power factor is used for accurate voltage drop calculations.
- A poor power factor will result in a higher voltage drop, especially for large cable sizes (because their impedance is highly reactive).
Cable length (m)
- This is the distance between the supply point and the load location.
- The cable return path length is automatically included with the voltage drop calculations for single-phase loads.
Cores
- The impedance (resistance and reactance) of single core and multicore cables is different.
Conductor
- You can select the conductor material of the cable. The type of conductor, due to different impedance values, affects the current-carrying capacity and the voltage drop of the cable.
Insulation
- The cable's insulation material affects the maximum allowable operating temperature and, hence, the current rating.
- Cables with a higher allowable temperature (which depends on the insulation type) will have a higher current rating.
