Table of Contents
Overview
Oil-filled cable fundamentals
Oil-filled cables are a part of the self-contained fluid-filled cable type family. The main insulation for this type consists of multiple layers of paper impregnated with oil (to prevent the formation of voids and the ionisation of these voids during energisation) and encased in a metal sheath. Single core oil-filled cables have a central fluid duct that allows the oil (dielectric fluid) to flow along the cable length. Three-core oil-filled cables usually have multiple fluid ducts embedded in the filler material between the cores, or if there is no filler the oil flows between the insulation of the cores and the outer metal sheath. An outer sheath (or jacket) is provided to prevent corrosion of the metal sheath.

Current rating calculations for oil-filled cables
- Model the oil-filled cable using cable component dimensions and material properties obtained from a manufacturer datasheet. Oil duct dimensions and fluid properties are not required for the current rating calculations.
- Calculate the AC resistance of the conductor as operating temperature.
- Calculate the electrical loss factors from the metallic layers in the oil-filled cable. The electrical loss of the sheath depends on the bonding arrangement.
- Calculate the dielectric losses inside the main insulation determined by the insulation capacitance and operating voltage.
- Calculate the internal thermal resistances T1, T2, and T3 inside the oil-filled cable.
- Calculate the external thermal resistance T4 based on the external thermal environment and the installation conditions. Note this can be done using the analytical equations in IEC 60287-2-1 [1], or alternatively using numerical finite-element calculations.
Example calculation
Cable model
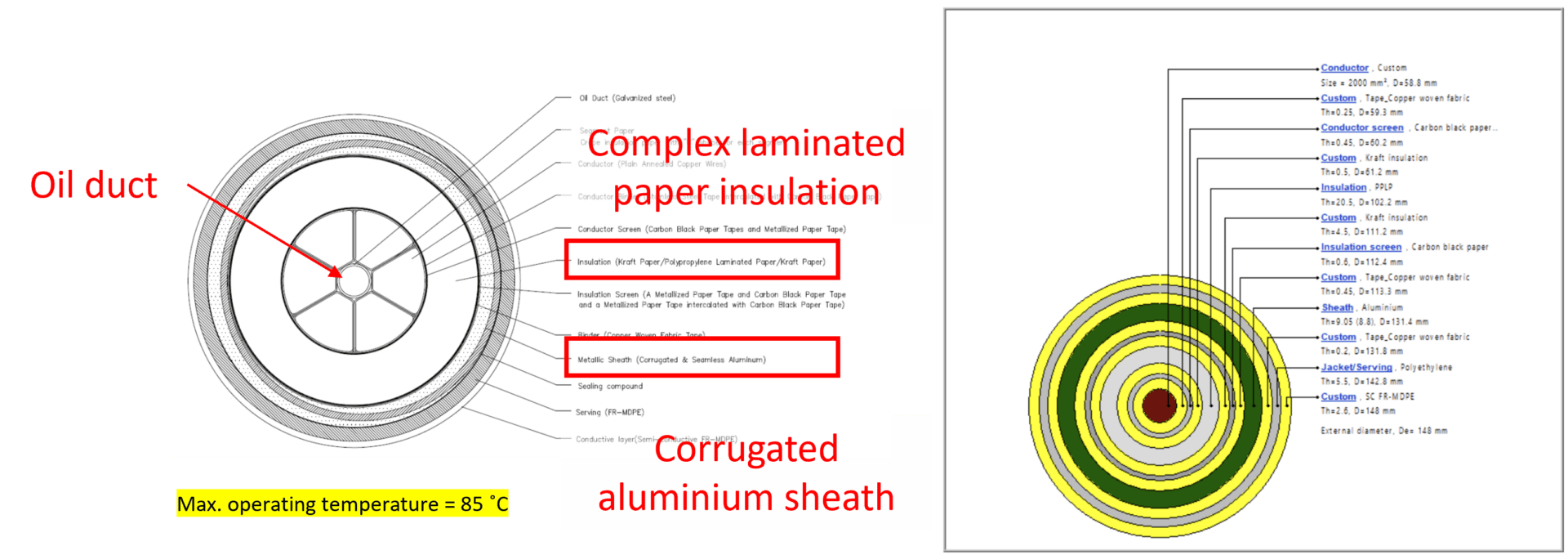
Figure 2 – Oil-filled cable software model
Installation conditions
| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Operating voltage | 400 | kV |
| Frequency | 50 | Hz |
| Buried arrangement | Trefoil, touching | |
| Burial depth (centre of trefoil) | 1 | m |
| Sheath bonding | Solidly bonded | |
| Native soil thermal resistivity | 1 | K.m/W |
| Soil ambient temperature | 20 | ˚C |
Calculated cable current rating
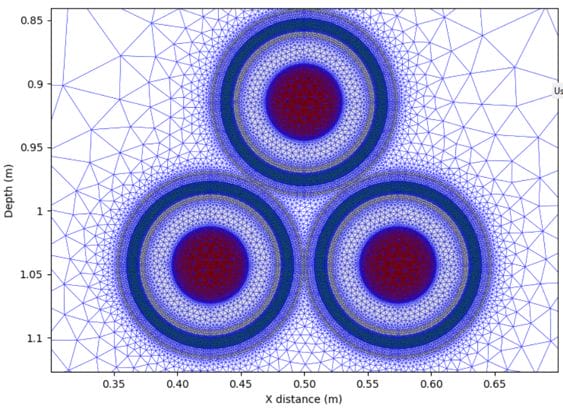
Figure 3 – Mesh plot from a finite element model of the oil-filled cables
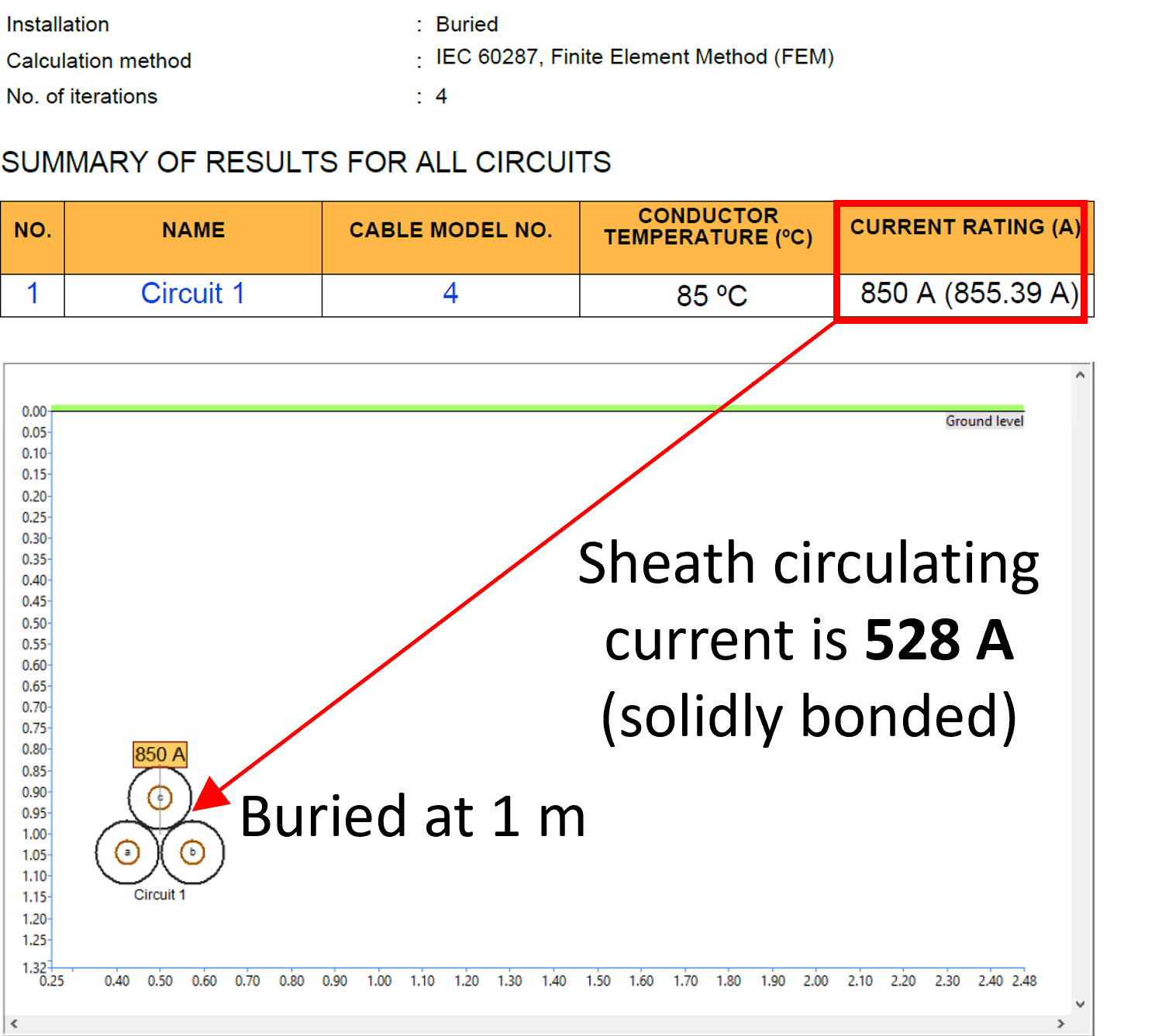
Figure 4 – Oil-filled cable current rating calculation result