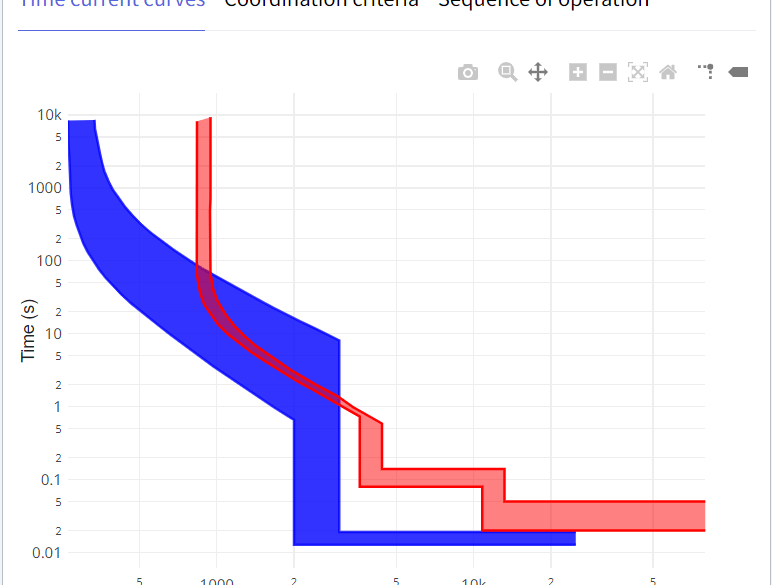
Accurately calculating voltage drop results in lower voltage drops which leads to smaller cable sizes and saves money.
You can calculate voltage drop by hand or using software.
Cable Pro Web software performs accurate voltage drop calculations. Try Now for Free.
To accurately calculate voltage drop in cables utilise:
- Conductor resistance, Rc (in Ohms/m) values based on actual cable operating temperature (from the actual current loading percentage).
- Conductor reactance, Xc (in Ohms/m) values. Xc = 0 for d.c. installations.
- Load power factor (cosθ).
- Accurate cable route length (L).
- Actual maximum operating load current (I).
For single phase:
For three phase:
The values for Rc and Xc are provided in the Standards.
The conductor resistance is lower when you consider the actual operating temperature. Using resistance values at the actual cable operating temperature results in more accurate and less conservative (lower) voltage drop than if you were to consider the cable to be at its maximum operating temperature.
References
Standard AS/NZS 3008.1.1 Electrical Installations-Selection of cables
Read our article: Voltage Drop Calculation Method with Examples