Indice dei contenuti
Who created this list of earthing Standards?
Experienced electrical earthing design engineers with years of hands-on project expertise have developed this reference list of standards for power systems earthing.
These professionals have drawn on their extensive knowledge to compile a comprehensive guide that ensures compliance, safety, and reliability across various applications. From substations to renewable energy systems, the standards outlined here reflect industry best practices and are tailored to meet the diverse needs of modern electrical installations.
Where do the important earthing standards come from?
1. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
The IEC is a global standards organisation that focuses on electrical, electronic, and related technologies. It develops internationally accepted standards that ensure compatibility, safety, and efficiency in power systems worldwide.
2. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
3. Australian/New Zealand Standards (AS/NZS)
4. British Standards Institution (BSI)
5. International Council on Large Electric Systems (CIGRE)
CIGRE is a global organisation dedicated to advancing power system technology through research and technical guidance. It provides specialised insights into grounding system design and lightning performance for transmission lines.
6. Energy Networks Association (ENA)
7. Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
List of Standards for Power Systems Earthing Design
Power systems earthing is a critical component of electrical safety and performance. Below is a comprehensive list of standards categorised by their specific applications, with additional standards included.
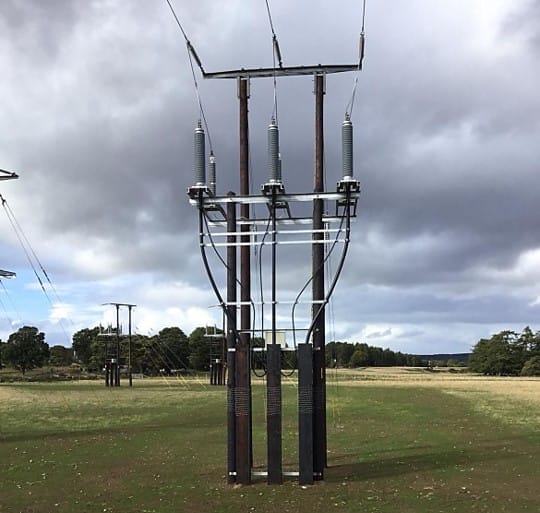
1. Substation Earthing
- IEEE Std. 80-2013: Guide for safety in AC substation grounding.
- AS/NZS 2067: Substations and high-voltage installations exceeding 1 kV AC.
- BS EN 50522:2022: Earthing of power installations exceeding 1 kV AC.
- ENA DOC 045-2022: Substation earthing guide (EG-1).
2. Testing of Earthing Systems
- IEEE Std. 81-2012: Guide for measuring earth resistivity.
- ENA TS 41-24:2018: Guidelines for design, installation, testing, and maintenance of main earthing systems in substations.
3. Touch/Step Voltage Limits
- IEC TS 60479: Effects of current on human beings and livestock.
- IEEE Std. 80-2013: Safety guide in AC substation grounding (also relevant here).
- ENA DOC 025-2022: Power system earthing guide (EG-0).
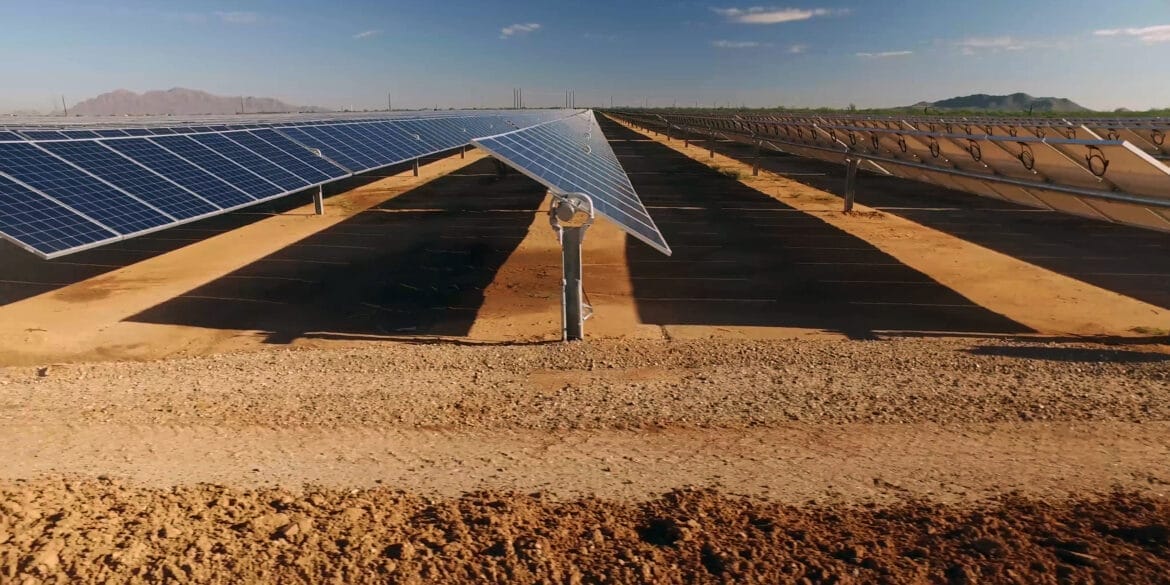
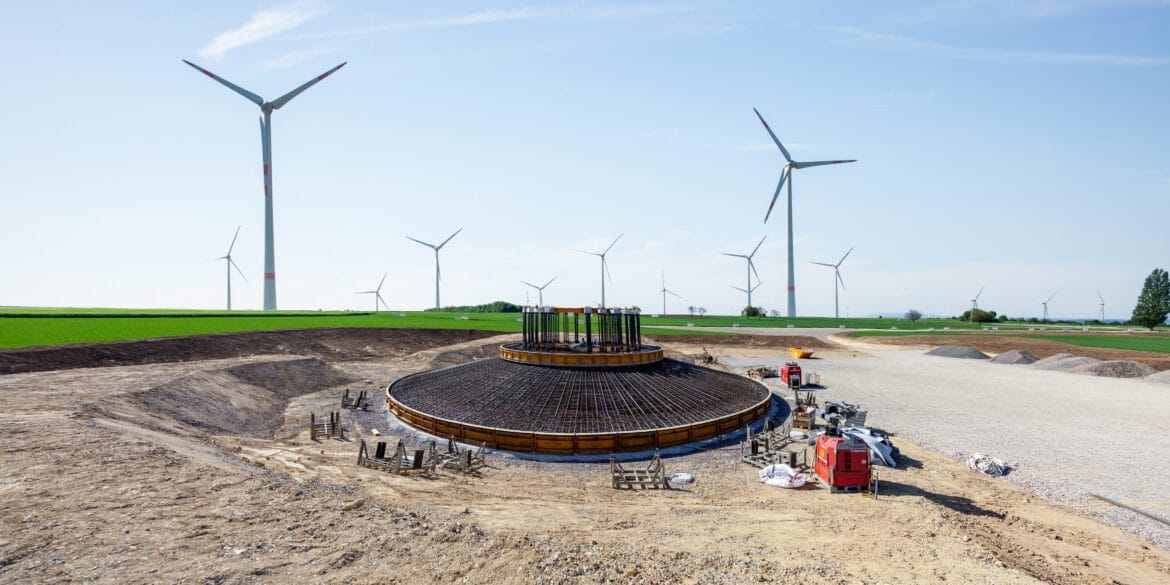
4. Renewable Energy Systems
- IEC 62305-3: Protection against lightning (wind turbine earthing).
- IEEE Std. 2870-2022: Wind power plant grounding.
- IEEE Std. 2778-2020: Solar power plant grounding.
5. Metallic Pipelines Safety
- AS/NZS 4853:2012: Electrical hazards on metallic pipelines.
- CIGRE TB 95: Influence of HV AC power systems on metallic pipelines.
6. Industrial & Commercial Earthing
- AS/NZS 3000 Standards Collection: Power system grounding of industrial and commercial installations.
- BS 7671 – 18th Edition: The IET wiring regulations.
- BS 7430:2011: Code of practice for protective earthing of electrical installations.
7. Overhead Lines
- AS/NZS 7000:2016: Overhead line design.
- CIGRE TB 781: Impact of soil-parameter frequency dependence on the response of grounding electrodes.
- CIGRE TB 839: Procedures for estimating the lightning performance of transmission lines.
8. High Voltage DC Systems
- EPRI EL-2020: HVDC ground electrode design.
9. Data Centres Earthing
- IEC 60364-5-548:1996: Earthing arrangements and equipotential bonding for IT equipment.
- IEEE Std. 1100–2005: Grounding sensitive electronic equipment.
10. Telecommunications
- AS/NZS 3835.1:2006: EPR (Earth Potential Rise) protection of telecommunications network users.
- BS EN 50310: Telecommunications bonding networks for buildings and other structures.
11. Fault Current Distribution
- ENA EREC S34–2017: Assessing the rise of earth potential in electrical installations.
- CIGRE TB 347: Earth potential rises in specially bonded screen systems.